Performing Allocations
Within Relyence RBD, for any RBD, you can perform Allocation analysis.
Allocation analysis in Relyence RBD allows you to set a reliability goal and determine how to most effectively achieve that reliability goal by distributing, or allocating, that goal across the block diagram's components. Allocation analysis is most helpful when a product is in the design phase.
To set up and perform Allocation analysis in Relyence RBD, select your RBD in the All RBDs pane and make sure the RBD tab is selected showing the block diagram. Then, from the Sidebar, select Tools>Allocation.
The Allocating dialog appears for the selected RBD, including the default or previous selections and results.
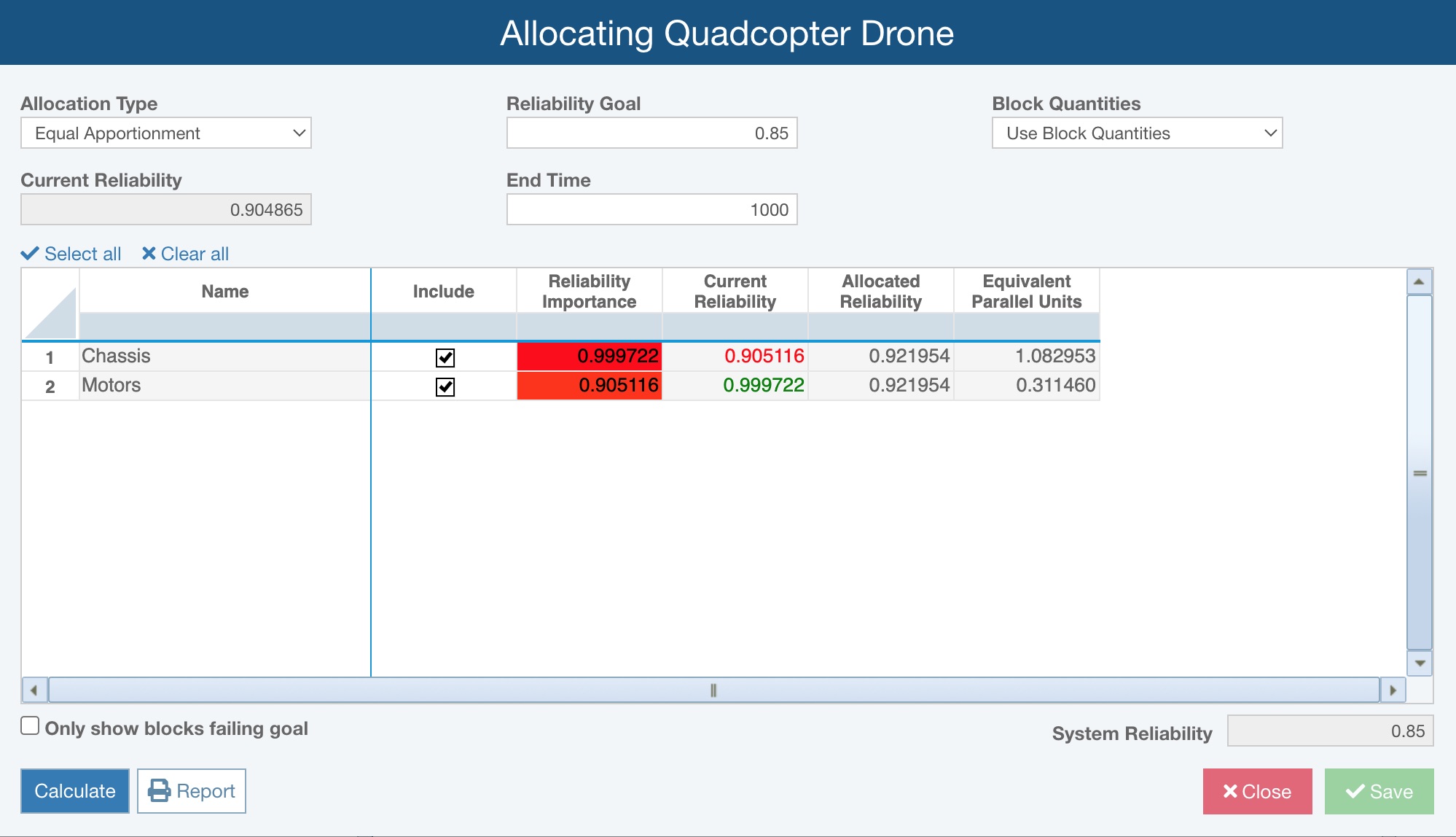
When considering Allocation calculations, you can set:
- Allocation Type - Relyence RBD Allocation analysis offers four Allocation Type choices:
- Equal Apportionment - the Reliability Goal is distributed equally across all blocks
- Balanced Apportionment - like in Equal Apportionment, the Reliability Goal is distributed equality across all blocks, however if a block's Current Reliability already meets or exceeds its Target Reliability, its Current Reliability will not be reduced in the Allocation analysis
- Weighted - The Reliability Goal is distributed across all included blocks based on the Weight factors entered
- Optimized - The Reliability Goal is optimally distributed across the included blocks based on a Feasibility factor; Feasibility indicates the difficulty of increasing each block's Reliability on a scale of 0.0 to 0.99; lower values mean it is more difficult (less feasible) to improve block performance, whereas higher values mean is is less difficult (more feasible) to improve block performance; note that the more difficult a block's reliability is to improve, the higher that associated cost would be
- Reliability Goal - the target Reliability for the system modeled in the RBD
- Block Quantities - option to specify how to use block quantity values when performing allocation calculations
- Use Block Quantities: quantity values assigned to blocks in the RBD are used
- Force Block Quantities to One: assumes quantity value for all blocks is 1
- End Time - the final Time to consider; this value generally represents the mission time for the system under review in the RBD
- Allocation Iterations - the number of allocation iterations that should be run; applies for only Allocation Type of Optimized only
Note that the Current Reliability show the calculated Reliability for the End Time for the RBD.
The input/results table will vary based on the Allocation Type. The table is shown below for Allocation Type = Equal Apportionment.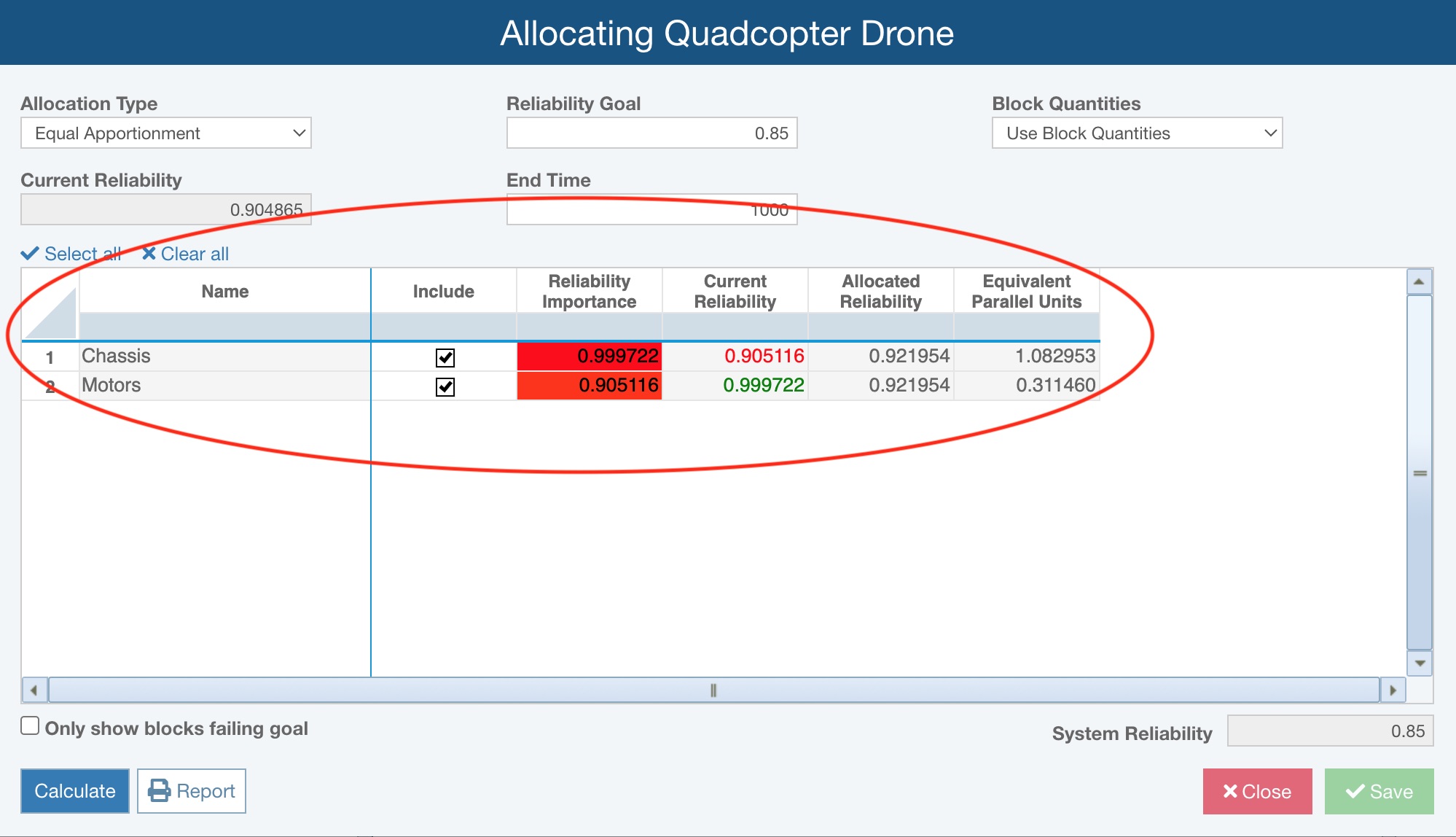
Note that the input/results table does vary based on the Allocation Type.
For all Allocation Types:
- the Name column will list the name of each Block
- the Include column lets you confirm which Blocks should be included in the allocations analysis
- Reliability Importance - a numerical result that indicates how much each block's Reliability factors into total system Reliability; in general, blocks with lower Reliability have higher Reliability Importance as an increase of such a block's Reliability has a greater effect on the overall system Reliability
- Current Reliability - displays the time-dependent Reliability value calculated for the RBD; the value will show in green font when it is greater than the Allocated Reliability and will show in red font when it is less than the Allocated Reliability
- Allocated Reliability - displays the calculated time-dependent Reliability value per the defined Allocations calculations
- Equivalent Parallel Units - indicates the number of equivalent parallel components (in a 1::n configuration) that would be required to achieve the block's calculated Allocated Reliability instead of increasing its reliability performance
For all Allocation Types except Equal Apportionment, Maximum Achievable Reliability can be specified to set the upper limit for the calculated Allocated Reliability value.
For Allocation Type Weighted, Weight is also considered, which is the weighting factor for the allocations calculations.
For Allocation Type Optimized, Feasibility is also considered; it indicates the difficulty of increasing each component's Reliability on a scale from 0.00 to 0.99 with lower values indicating it is more difficult (i.e. less feasible) to improve component performance.
You can also set Only show blocks failing goal, which will result in the table showing only the blocks where the Current Reliability is less than the Allocated Reliability.
The System Reliability is displayed.
At the bottom of the Allocating dialog, you can use the following buttons:
- Calculate - click Calculate to run the Allocation calculation based on the parameters established on the Allocating dialog
- Report - click Report to run the Allocation report
- Close - click Close to return to the RBD pane
- Save - click Save to save all unsaved changes on the Allocating dialog
Allocating Report
When you click Report on the Allocating dialog, the Report Options dialog appears.
Specify the Report Title and click Report to generate the report.
The Allocation report is shown in a new browser tab. A sample is shown below.
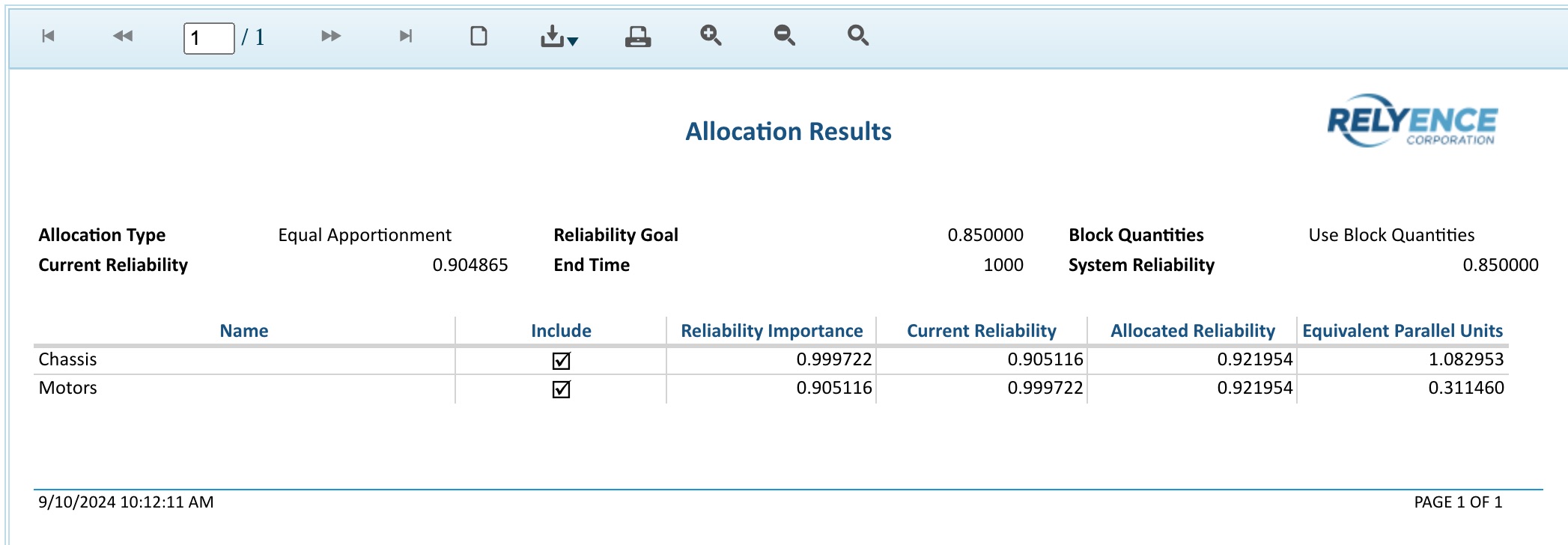
Close the browser tab to exit the report preview and return to Relyence.
When you have completed your allocation analysis, use the Save and/or Close buttons to save the inputs if you prefer and close the Allocating dialog.