Importing and Exporting Fault Trees
You can import and export your Fault Trees.
Importing
You can import data from a Microsoft Excel (.xlsx file) spreadsheet into Relyence. The import is a multi-step process, and Relyence will guide you through the steps to import your data.
Click Import>Fault Tree Diagram.
The Import dialog appears.
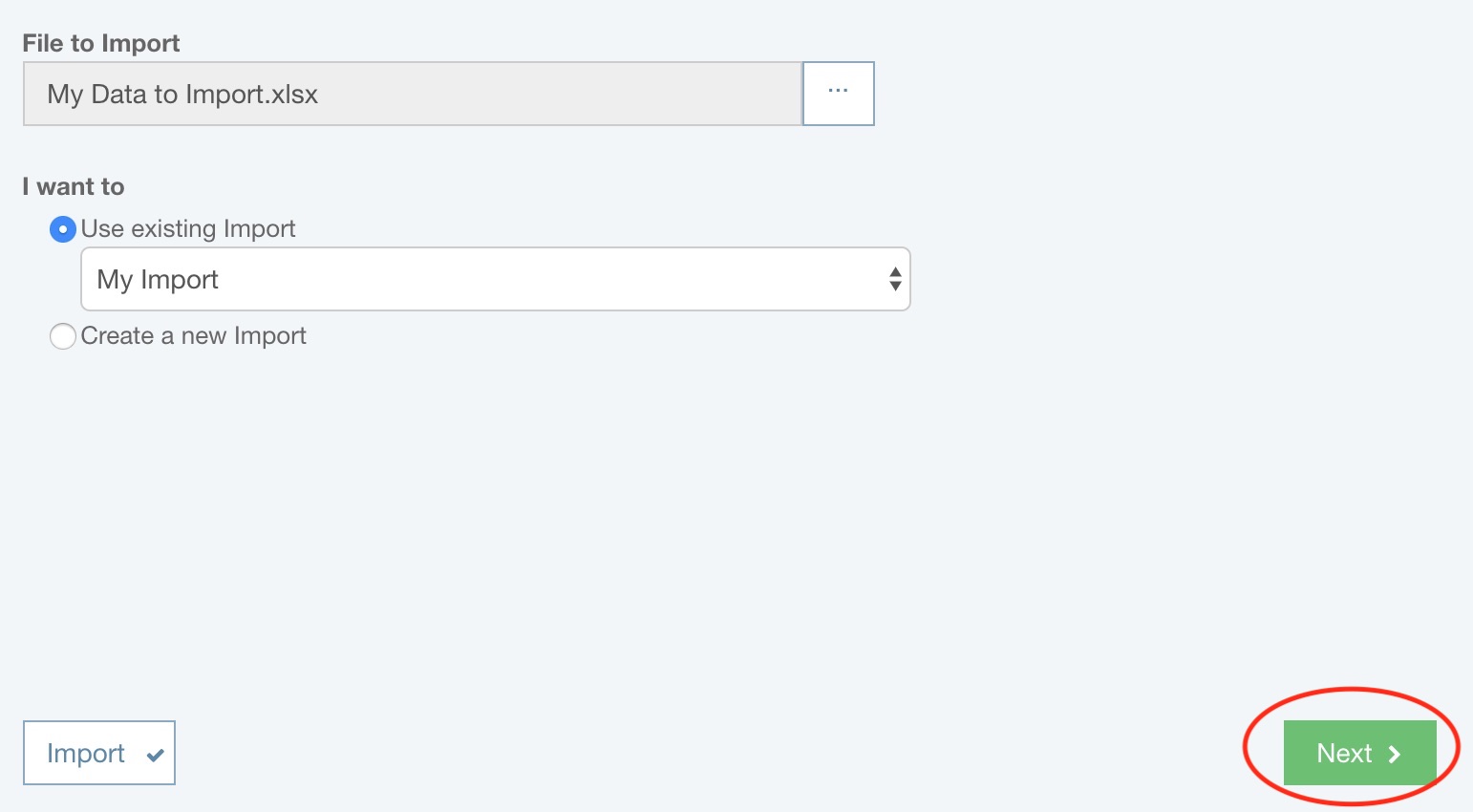
Step 1: Select the file to import and whether you want to reuse an existing Import
Select the File to Import. Click on the File Select (...) button to bring up the file explorer dialog. Navigate to the file you wish to import and select it.
If you have not yet performed and saved any Imports, no further data is requested. Click the Next button to proceed.
Otherwise, you can select either Use existing Import or Create a new Import.
If you do not want to reuse an existing Import, select Create a new Import and click the Next button.
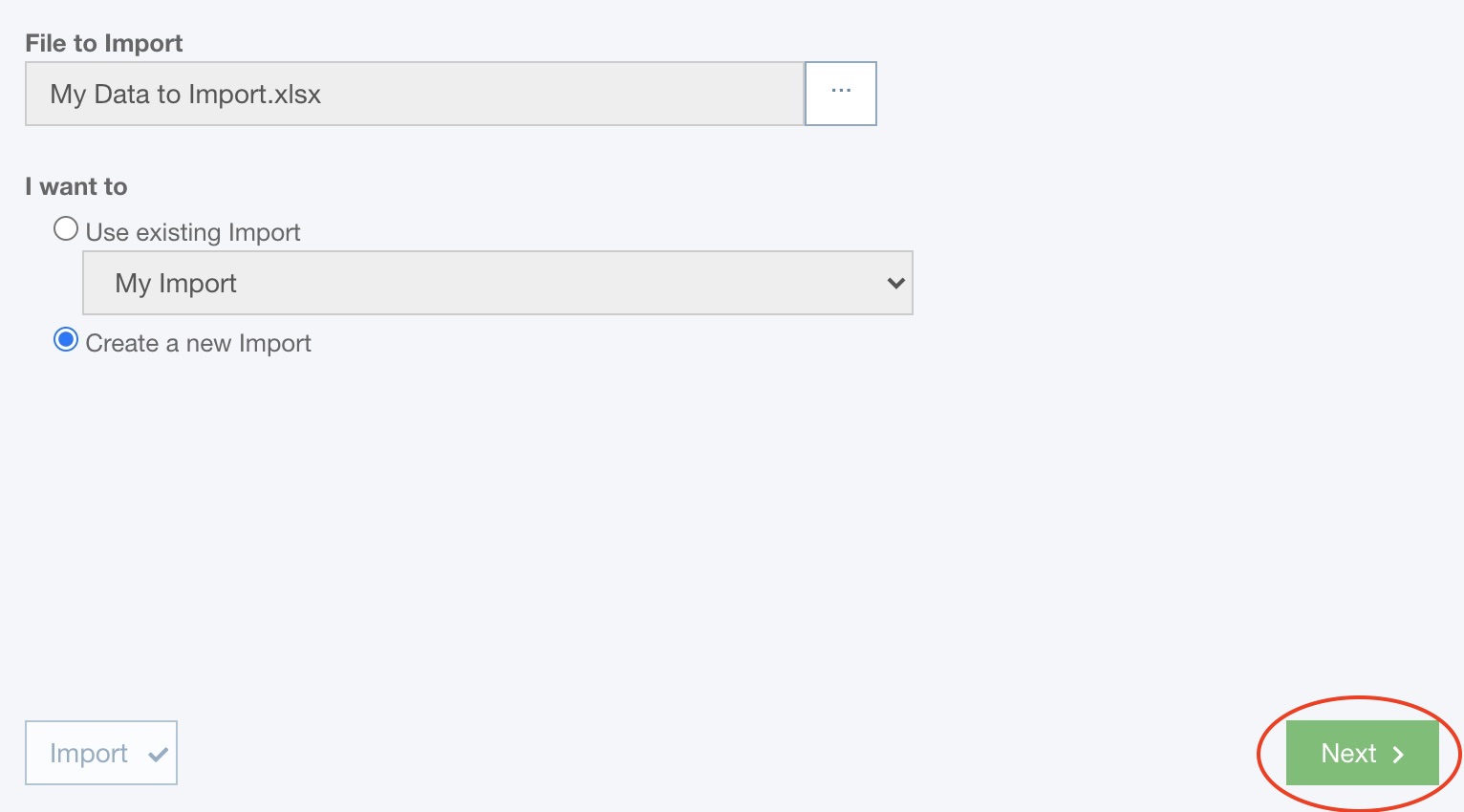
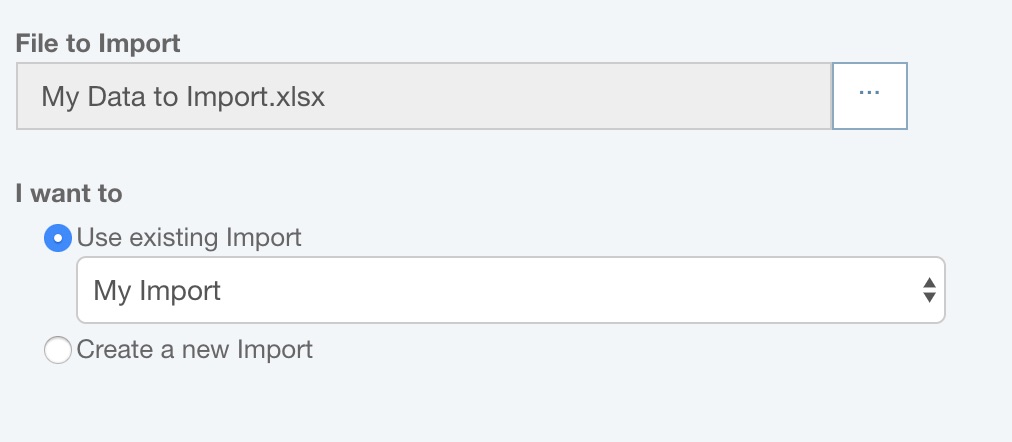
If you want to reuse an existing Import, select the Import you wish to use from the dropdown list of choices.
At this point, the Import button will be enabled, and you can choose to directly proceed to the data import step. This bypasses the import mapping steps and allows easy reuse of saved Imports.
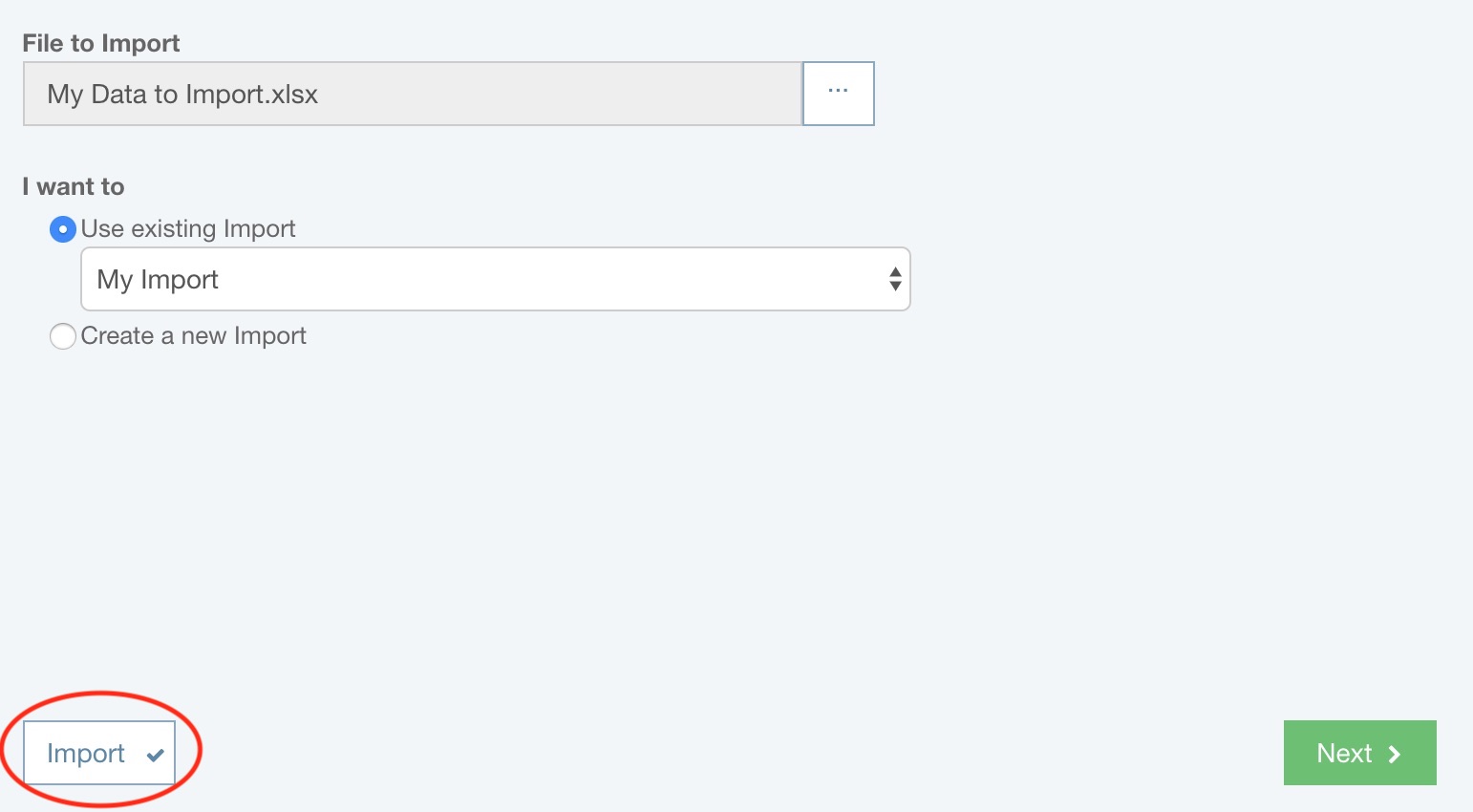
Otherwise, click the Next button.
Step 2: Select if you want to add or update records
If prompted, choose whether you want to add or update records during importing.

Note: The option to Add or Update records does not apply when importing Weibull Life Data or Weibull Reliability Growth Data.
If you choose to Add records, all line items in your import file will be added to your Analysis.
If you choose to Update records, the import will proceed by locating matching items from your import file in your Analysis, and then updating the matching records with data in the import file.
For Reliability Prediction importing, if you select Add records, you can optionally select Split Parts into multiple records by Quantity. When cleared, even if Quantity is greater than 1, a single Part record will be imported from the row with the Quantity value; whereas, when checked, if the Quantity is greater than 1, Relyence will import multiple identical Part records equal to the Quantity value. For example, if Quantity = 3, there will be 3 identical Part records created during the import. Additionally, if the Reference Designator is imported, comma separated Reference Designators can be separated and assigned to single Parts. This option is ideal for importing Parts lists to Relyence Reliability Prediction when part-level FMECA is also planned.
For FRACAS and Reliability Prediction importing, if you select to Update records, you can optionally select to Add new records during update. In this case, if a matching item from the import file is not found in the Analysis, a new record will be added.
Note that if you are importing DFMEA Worksheet or PFMEA Worksheet data, an extra choice will appear in addition to Add records and Update records - Add new Failure Mode records to existing Functions or Add new Failure Mode records to existing Process Steps. For more details on this type of import, see Importing New Failure Mode Records to Existing Function or Process Step Records.
Note that if you are importing Control Plan data, an extra choice will appear in addition to Add records and Update records - Add new Control Plan records to existing Process Steps. For more details on this type of import, see Importing New Control Plan Records to Existing Process Step Records.
Update Records
In order to update records during importing, the import file must include identifier data fields. These fields provide a unique identifier to locate the record to update. Because data fields such as Name are not required to be unique, these unique identifier fields are needed. Typically, these are referred to as "ID" fields.
The process to perform an import update are:
- Export with the Export all data fields option selected. This option will automatically include the unique identifier fields.
- Make the necessary changes to the exported file.
- Re-import using the Update records option.
The data fields that are required to perform a Update are:
- FMEA: Function ID at a minimum, also Mode ID, Cause ID, Effect ID, or Action ID if updating Mode, Cause, Effect, or Action records.
- FRACAS: Incident ID for Incidents, Problem ID for Problems.
- Fault Tree: ID
- Reliability Prediction: Part ID
Connect records
Note that if you are importing DFMEA Worksheet data, an extra choice will appear - Connect Effects to higher level Failure Modes. For more details on this type of import, see Connecting Effects to Higher Level Failure Mode Records in DFMEA.
Merge duplicate rows
If your FMEA Worksheet has consecutive duplicate rows, you can optionally check to have Relyence merge duplicate rows so as to create one record upon import.
For DFMEA and FMEA-MSR, you can merge duplicate rows for Functions, Failure Modes, Effects, and Causes. For FMECA, you can merge duplicate rows for Functions and Failure Modes. For PFMEA, you can merge duplicate rows for Process Steps, Failure Modes, Effects, and Causes.
Step 3: Map data fields
The Import Mapping dialog appears. In this dialog, you will see your data. If Column names contained in row is selected, select the row number and Relyence will attempt to automatically map your data columns. Any columns unrecognized will be unmapped. The number of unmapped columns will appear in the upper right and all unmapped columns will appear with a red border.
To map any unmapped columns, or remap a column, click the dropdown list at the top of the column and select from the list of available data fields. The type of data field will be indicated by the icon to the left of the data field name. The first icon in the list is always the crossed out "skip", or "do not map", indicator. The "A" icon indicates a text field, the Relyence logo icon indicates a unique Relyence database field, the "1" icon indicates a numeric field, and the "check mark" icon indicates a yes/no field.
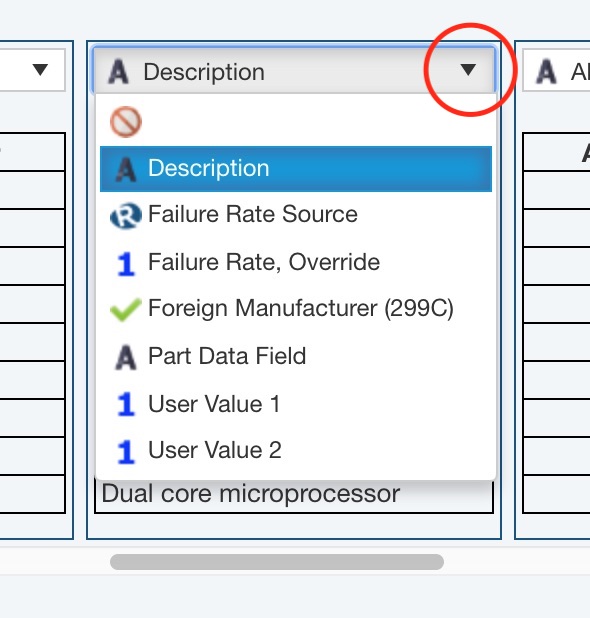
When you have completed mapping all your data, click Next.
Step 4: Optionally save Import and begin import process
The Save Import dialog appears. If you want to save this Import for later use, select Save this Import and enter the name for your Import. The number of columns to be imported and skipped will be shown.
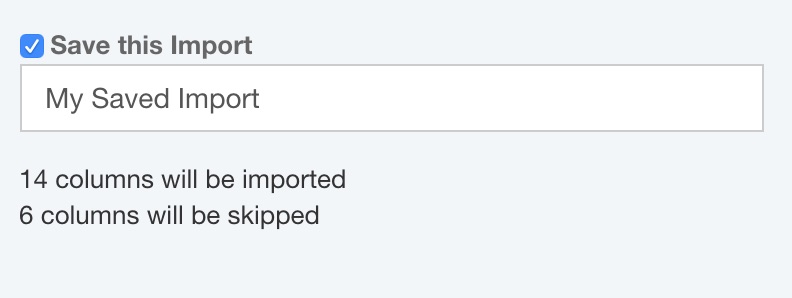
Click Import.
The import process will start up automatically, and the data will be imported. A progress indicator will appear as your data is being imported. When importing is finished, the Import Complete dialog appears.
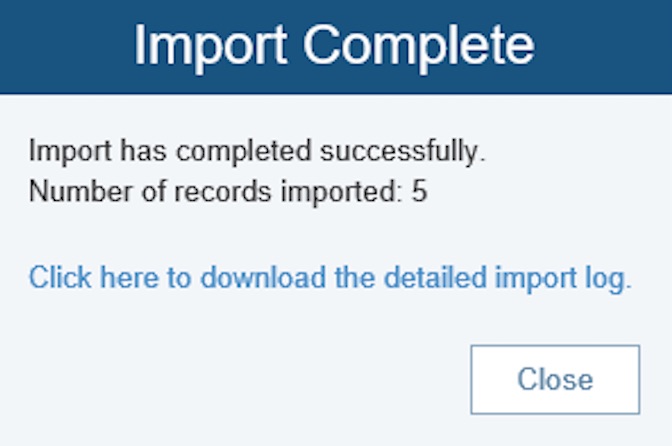
If successful, the number of records imported will be noted. If you want to view the import log, click the download link. If unsuccessful, the Import Complete dialog will note this. To view the import issues, click the link to download the import log and review the error(s) encountered during import.
If no valid data can be found in a row of your Microsoft Excel file, no new item will be added; i.e. there will be no "blank" data records imported into your Relyence Analysis.
Step 5: Complete import process
Click Close to close the Import Complete dialog.
Importing data may take a few minutes depending on the size and complexity of the data you are importing.
An easy way to ensure your Microsoft Excel import file is properly set up is to use the Export function to create a sample file. You can then use this file as a starting point for creating your import file. You can then remove fields you don't use or need, change the order of the fields as you prefer, and add your data.
Click the following link if you would like to download and review a sample Fault Tree import file:
Managing Imports
During importing, you have the option to save your Import. If you would like to delete or rename any of your saved Imports, you can do so from Manage Analyses. For general details about the Manage Analyses feature, see the Help topic Using the Manage Analyses Function.
To access the Manage Analyses function, click Manage Analyses from the Account menu.
A list of all your current Imports will be shown, along with the Product type they are associated with, and the type of data that is imported.
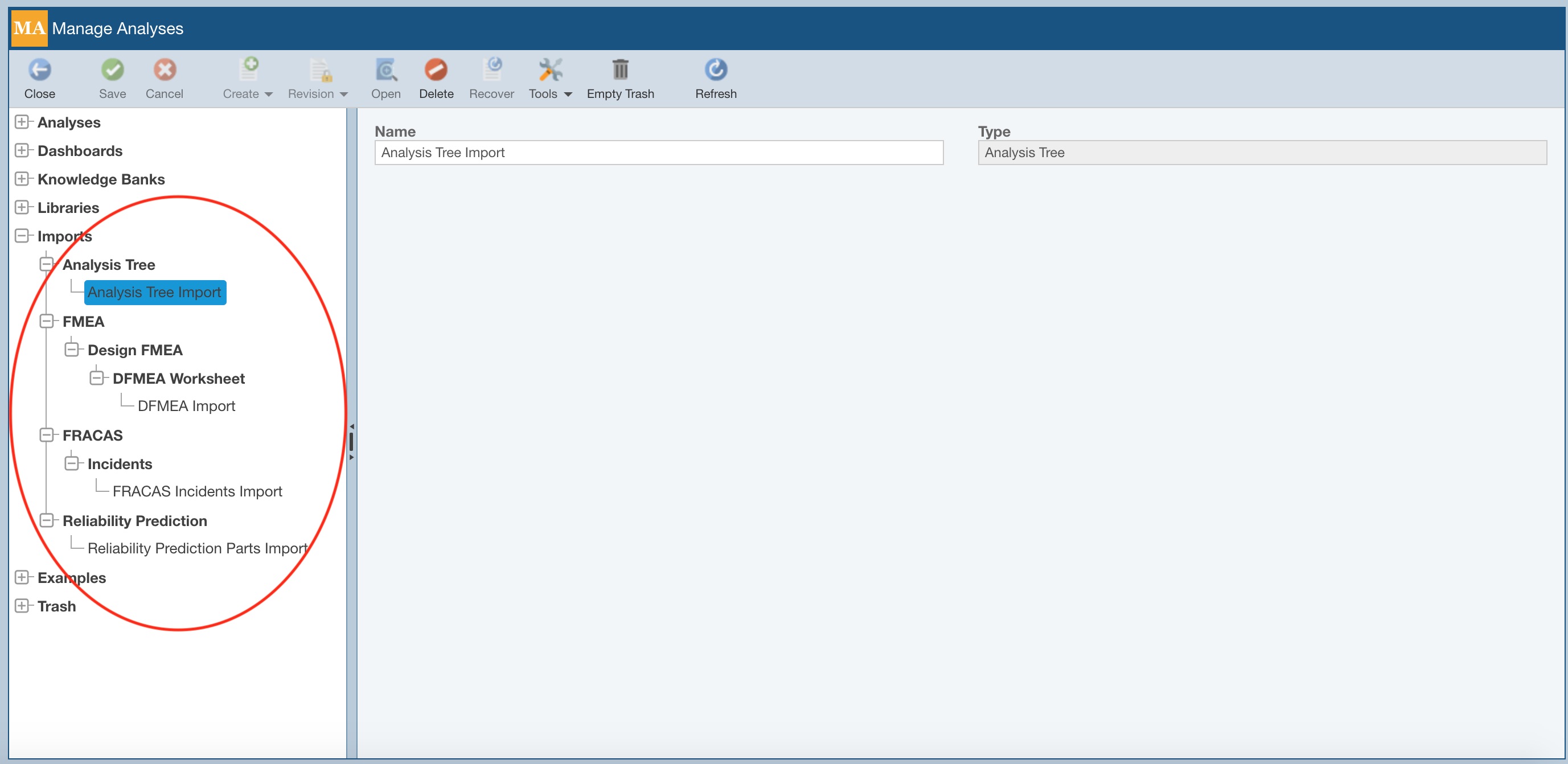
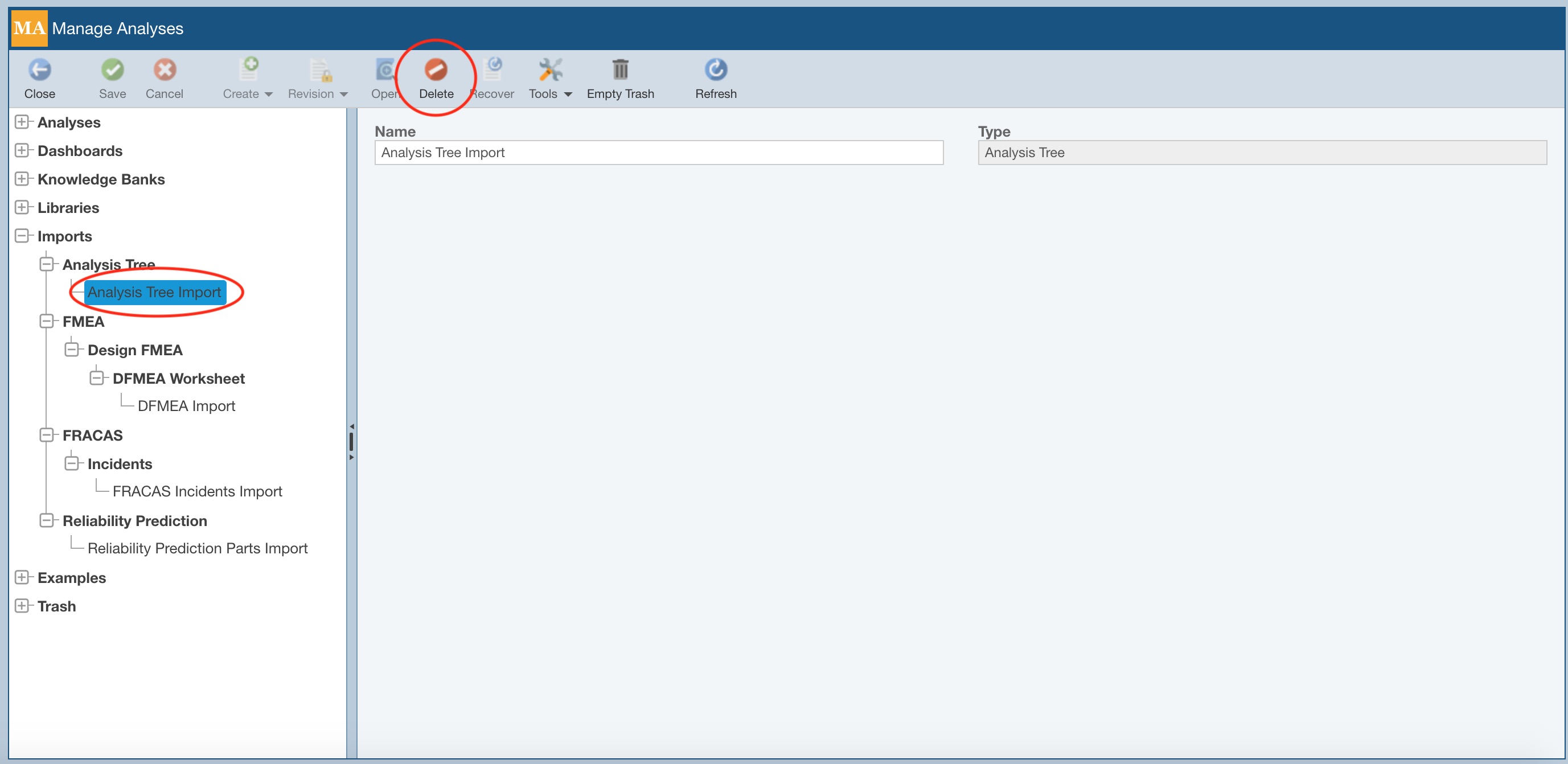
To delete any of your Imports, select it and click Delete. On the Delete dialog, click Yes to confirm the deletion or No to exit and retain the saved Import.
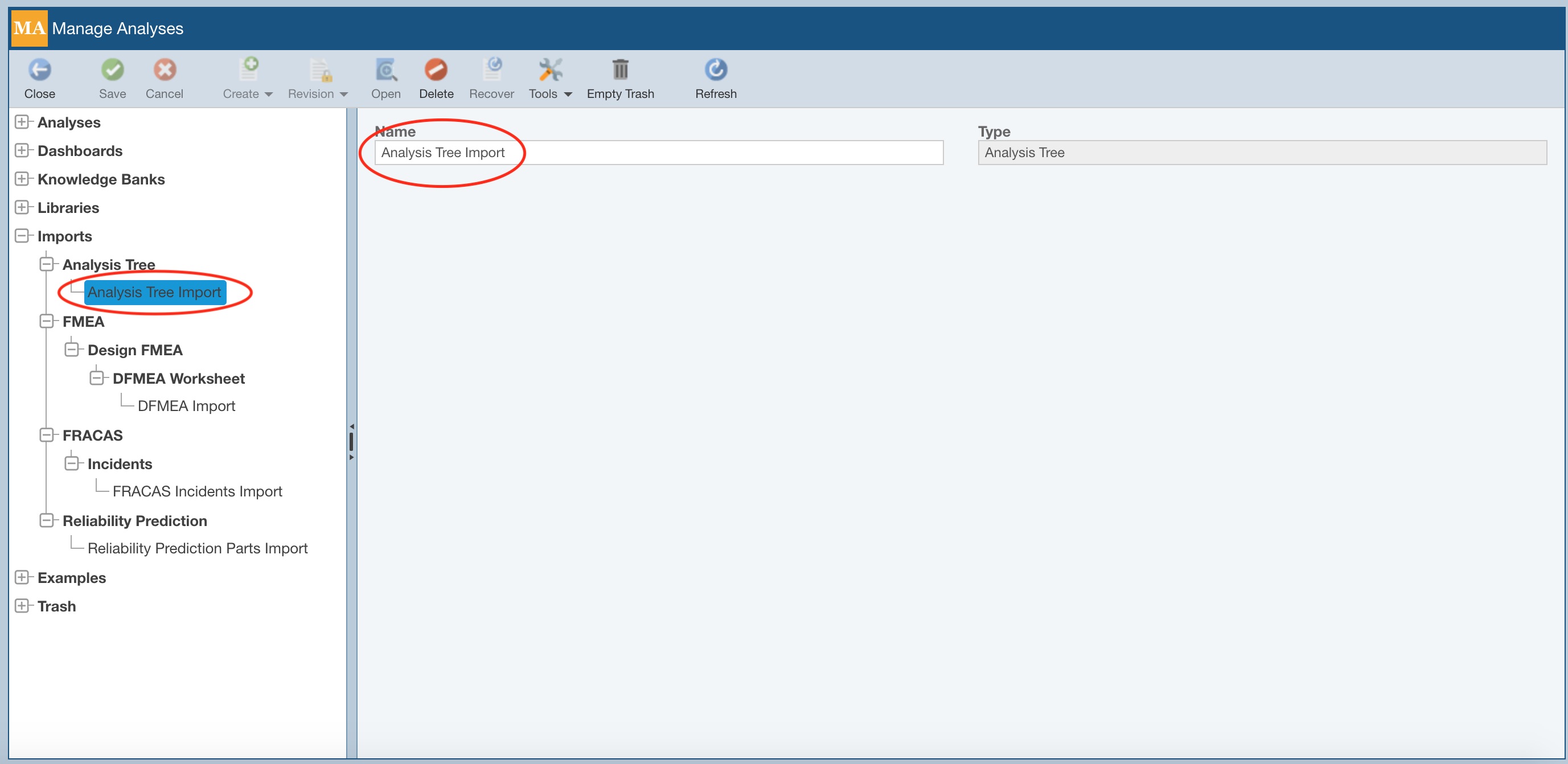
To rename any of your Imports, select it and in the rightmost pane, enter a new Name for the saved Import.
To exit Manage Analyses and return to your Analysis, from the Sidebar, click Back to Analysis.
Exporting
To export fault tree data, on the Sidebar, click Export and then Fault Tree Diagram.
The Export dialog appears.
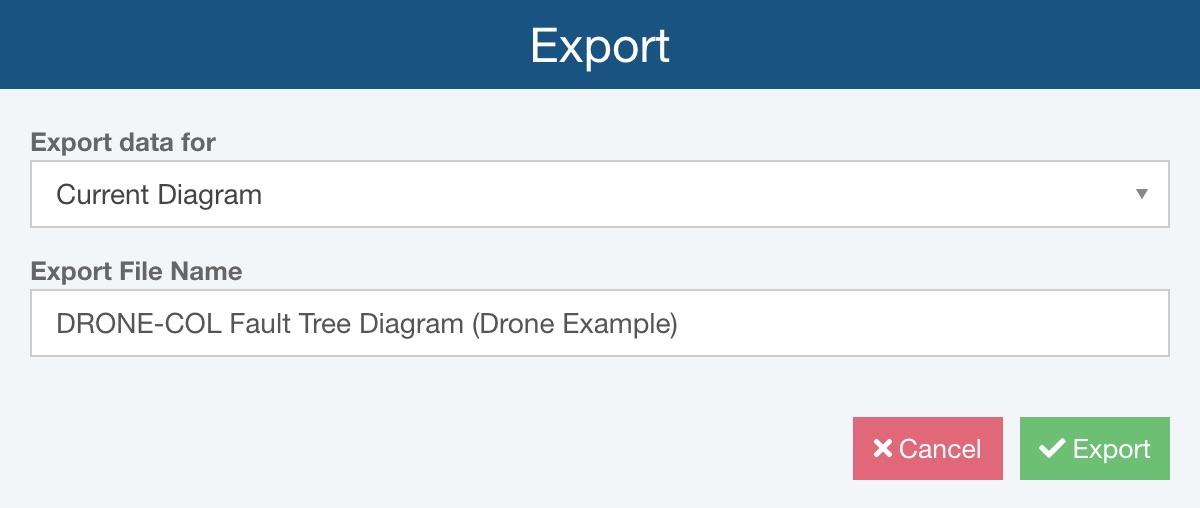
For Export data for, select Current Diagram or All Diagrams.
In the Export File Name field, you can enter the name for the exported file or accept the default.
Click Export to start the export process. A progress indicator appears.
If needed, click Cancel to stop the export.
When complete, the exported Microsoft Excel file will be available in your default download location.
The first row in the exported file will contain the data field names and the data for either the Current Diagram or All Diagrams.