RISK ANALYSIS
Relyence Fault Tree provides a powerful platform for constructing fault tree diagrams, modeling input events, and performing a variety of calculations to assess the likelihood of undesired events and the combinations of contributing factors that would cause those undesired events. Relyence Fault Tree provides the capabilities you need for comprehensive risk assessment using fault tree techniques.
Fault Tree Construction Made Easy
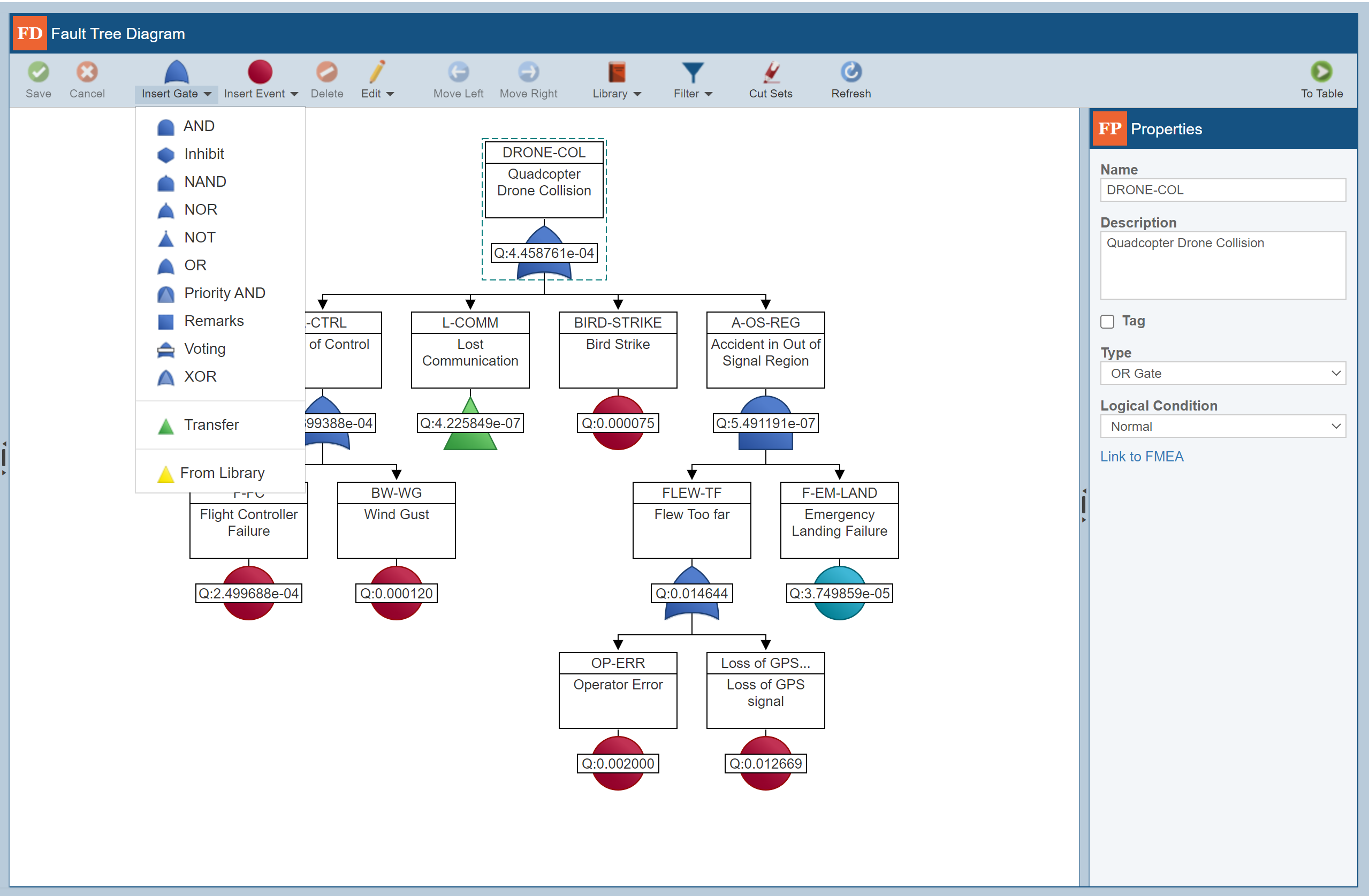
Relyence Fault Tree provides a user-friendly diagramming interface that enables you to quickly build your fault trees with ease. Select your gates and events and use our efficient interface to add them to your diagram. Relyence Fault Tree then optimally lays out your tree, auto-aligns, auto-connects, and adds color and graphics to enhance your diagram. The Relyence Fault Tree Diagram Editor does the work for you so you can concentrate your efforts where they are most effective: on your risk assessment activities.
Logic Gates & Events
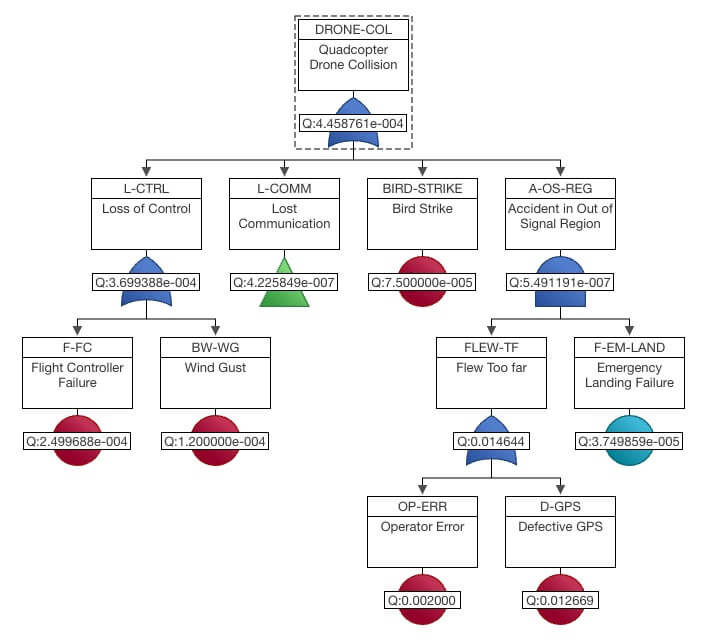
At the heart of fault tree analysis is the set of logic gates and events used in diagram creation. Relyence Fault Tree supports a comprehensive set of logic gates. Gates types include AND, Inhibit, NAND, NOR, NOT, OR, Priority AND, Remarks, Voting, XOR, and Transfer. Event types include Basic, House, Undeveloped, and Repeat. Relyence Fault Tree also supports an expansive set of input models including failure rate, failure rate with repair, asymptotic unavailability, constant probability, constant mission time, frequency with failure rate, lambda tau, latent repairable, and mean unavailability.
High-Powered Conventional FTA Analytics
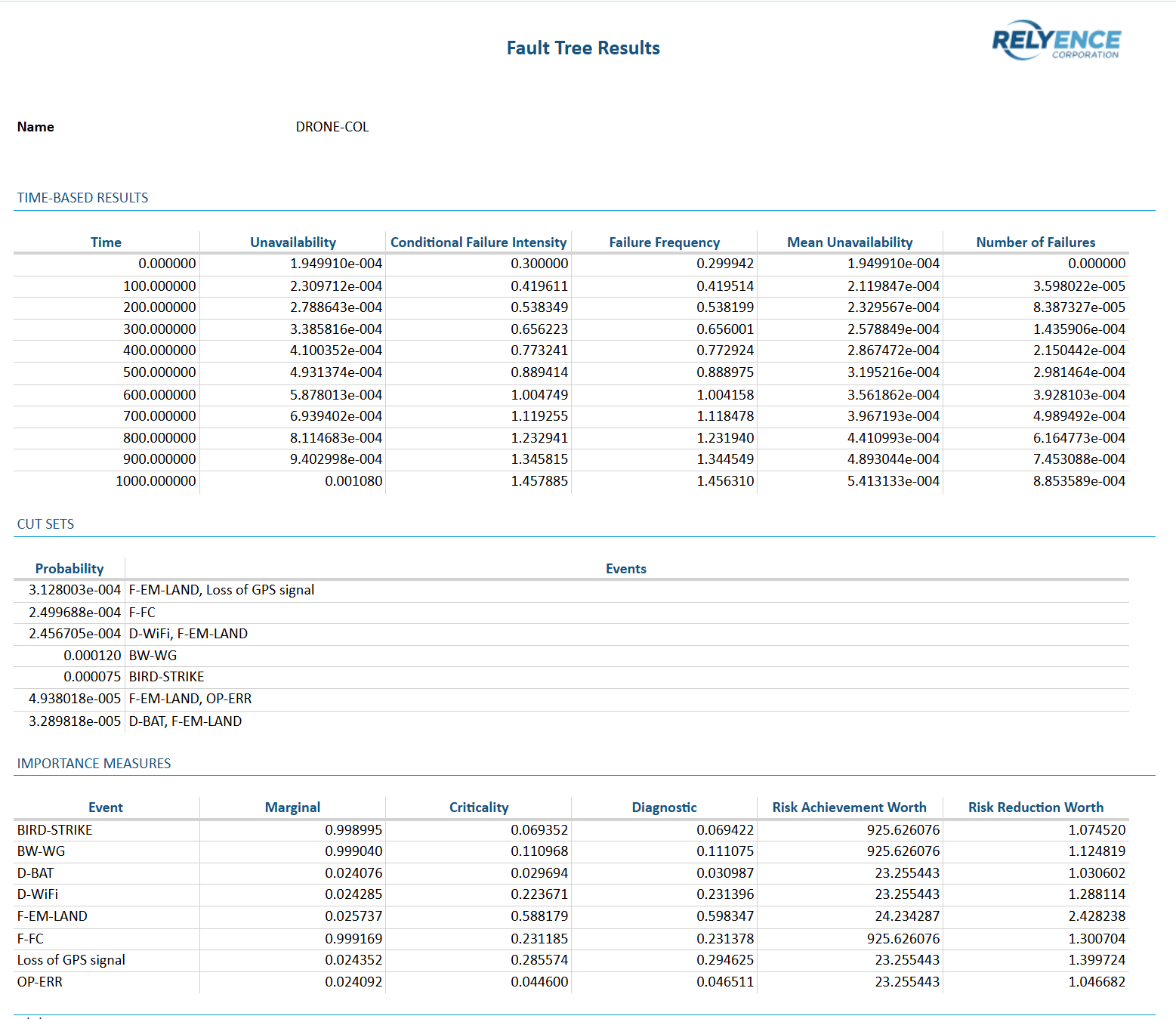
Coupled with impressive diagramming capabilities, the Relyence Fault Tree high-powered calculation engine supports a broad range of computation methods and the calculation of a variety of risk and safety metrics. You can select to calculate a number of critical risk measures including minimal cut sets (MCS), unavailability, failure frequency, conditional failure intensity, and number of failures. You can choose from a list of supported calculation methods including exact, simulation, cut set summation, cross product, and Esary Proschan. For simulation analyses, you can specify the number of simulation iterations to control the simulation engine. For cut set analyses, you can set cutoff values to optimize calculations. You can also include importance measures computations if you desire.
ARP4754A / ARP4761 Calculations
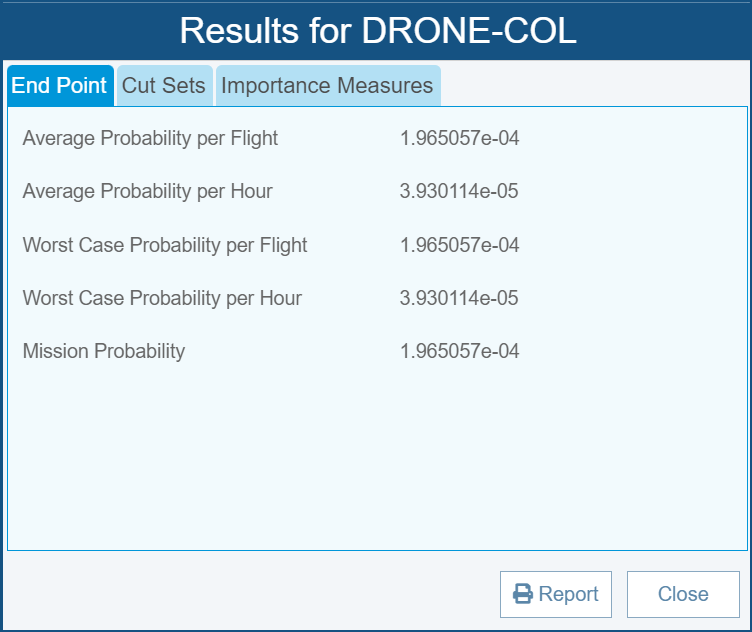
The SAE documents ARP4754A, entitled “Guidelines for Development of Civil Aircraft and Systems”, and ARP4761, entitled “Guidelines and Methods for Conducting the Safety Assessment Process on Civil Airborne Systems and Equipment”, provide recommendations and techniques for performing safety analysis on civil aircraft and systems to assess their safety performance throughout their lifecycle. They provide information on various methods, including using Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) to perform techniques such as the Preliminary System Safety Assessment (PSSA) and System Safety Assessment (SSA). When performing FTA based on the ARP4754A and ARP4761 guidelines, the top event is often an undesired event that occurs within a flight, such as an equipment malfunction or faulty reading. As such, FTA calculations are often given as the probability of the top-level event occurrence per flight or per flight hour.
Relyence Fault Tree can perform FTA based on the ARP4754A and ARP4761 guidelines, including support for Exposure Time (also known as at-risk time), Latent Failures, and Monitors. Additionally, the useful Monitor Library allows you to save a monitor with its associated parameters for later use.