Fault Tree Libraries
Relyence Fault Tree Libraries provide a powerful way to encapsulate fault tree data for reuse, efficient data management, and archiving. By enabling you to save fault tree diagrams, individual events, and/or monitors into a searchable databank, you can keep control of your data, reduce errors, and make diagram construction quick and effortless.
Fault Tree Libraries
Relyence Fault Tree Libraries allow you to save your fault tree diagrams and all encapsulated data for reusability, management, and archiving.
For example, you may have complete diagrams, portions of fault tree diagrams, or subdiagrams, that are used across multiple analyses. Or, you may want a place to store and maintain fault tree information for reuse in future analyses.
With a click of a button, you can save your fault tree diagrams to a Fault Tree Library. This databank of vital fault tree data is then available for you to retrieve and reuse as needed.
You can create and manage as many Fault Tree Libraries as you want. For example, you may want to use separate Libraries for separate products or processes. Or, separate teams may want to independently manage their own Libraries.
Event Libraries
When constructing fault trees, the lowest level in your diagram is represented by events. Events allow you to model any type of failure – such as a hardware failure, human error, system fault, or any failure event you choose. The behavior of events is described by using mathematical models and related parameters.
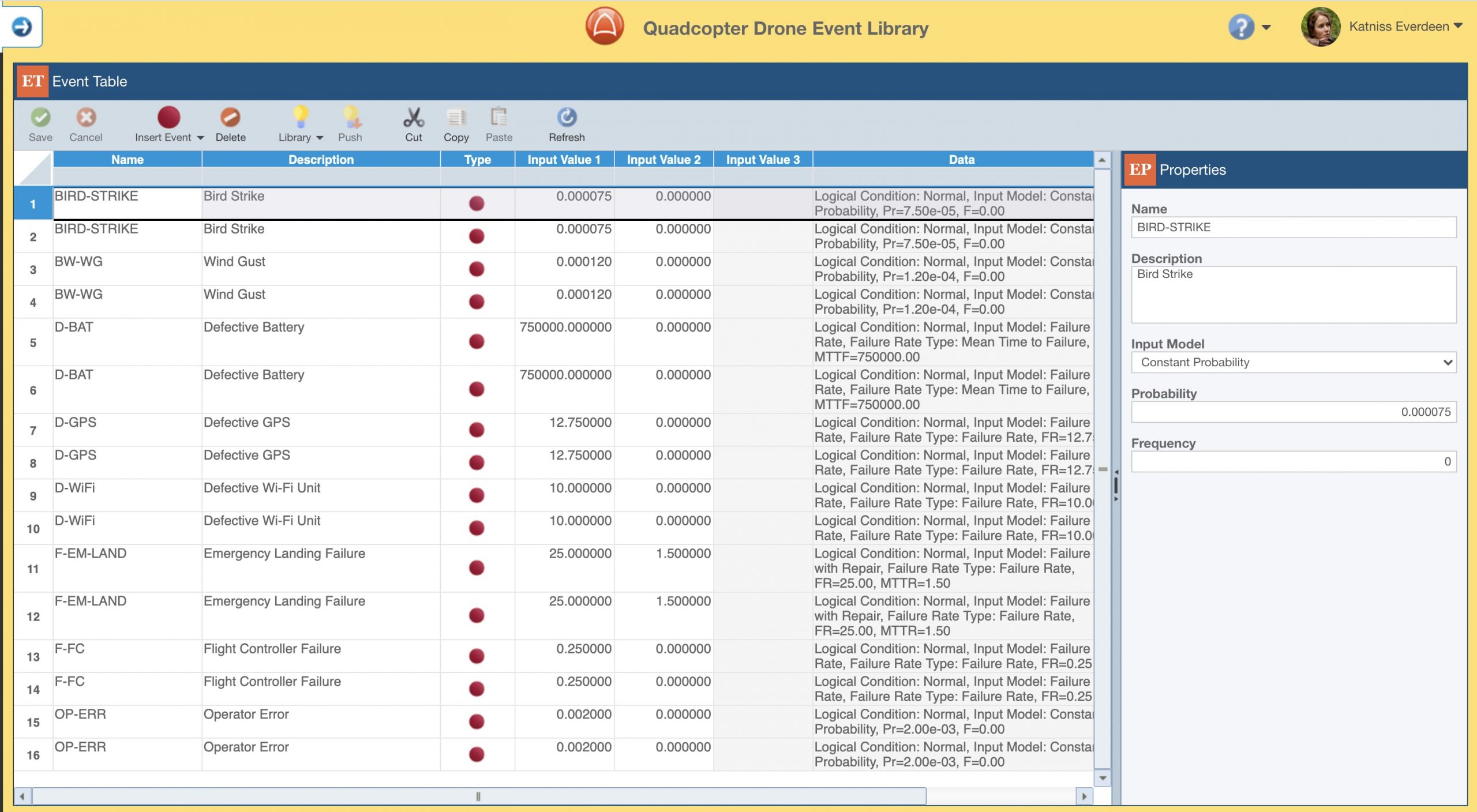
Relyence Event Libraries enable you to store a collection of described events for later reuse. Not only does this make fault tree construction more efficient, it also ensures data consistency.
As with Fault Tree Libraries, you can choose to create and manage as many Event Libraries as you prefer.
Building Fault Tree Libraries
You can build up your Fault Tree and Event Libraries in several ways.
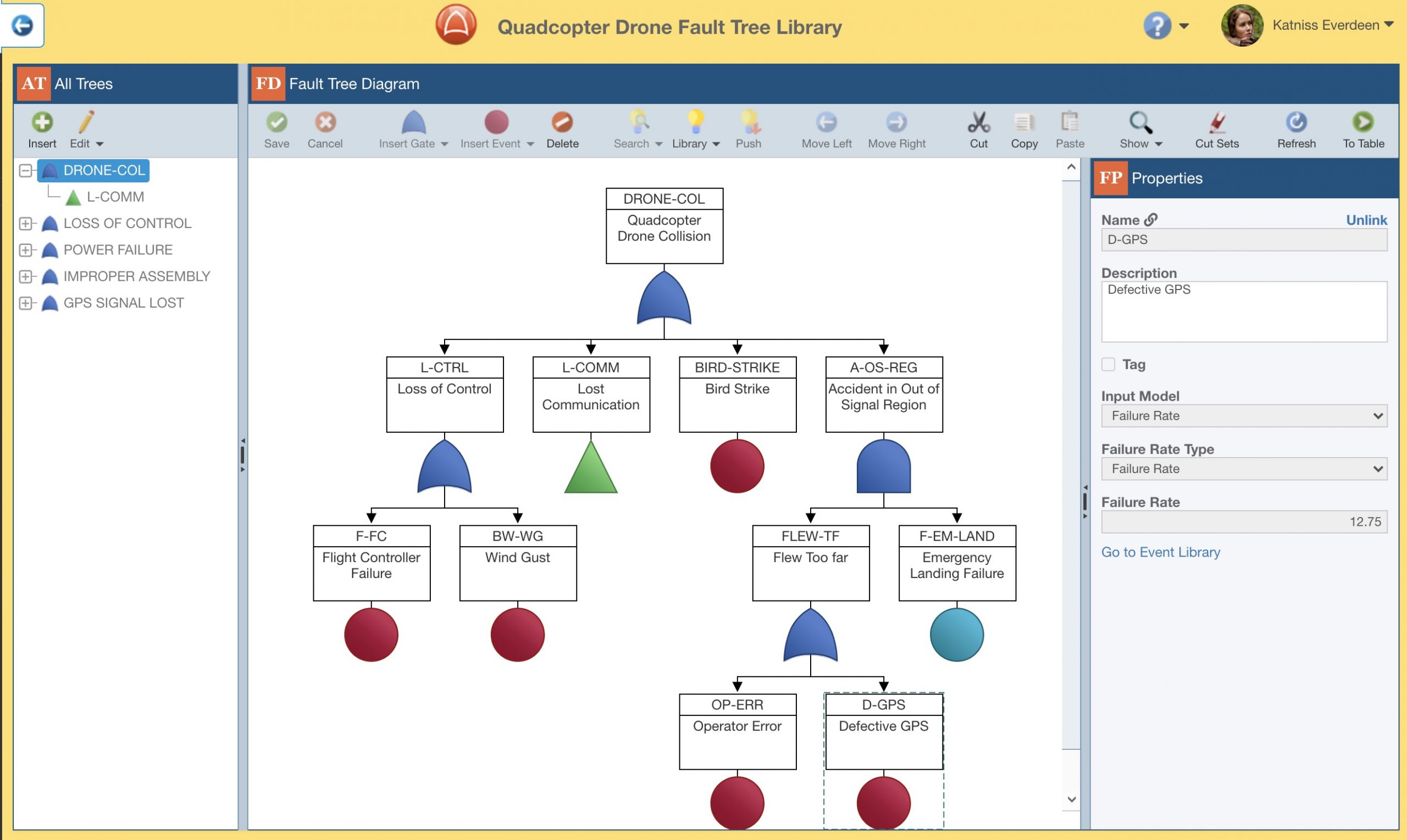
First, the easiest and quickest way to create a Fault Tree or Event Library is to build it directly based on an existing Fault Tree Analysis (FTA). This is a simple one-click process: just select the Build Library function and Relyence will automatically generate a Library for you based on your FTA.
Alternatively, you can create and open a new Library and directly enter the Library data using the Library interface. The Library interface mimics the standard, easy-to-use Relyence Fault Tree user interface, so it is an easy process to build up your Library in this manner.
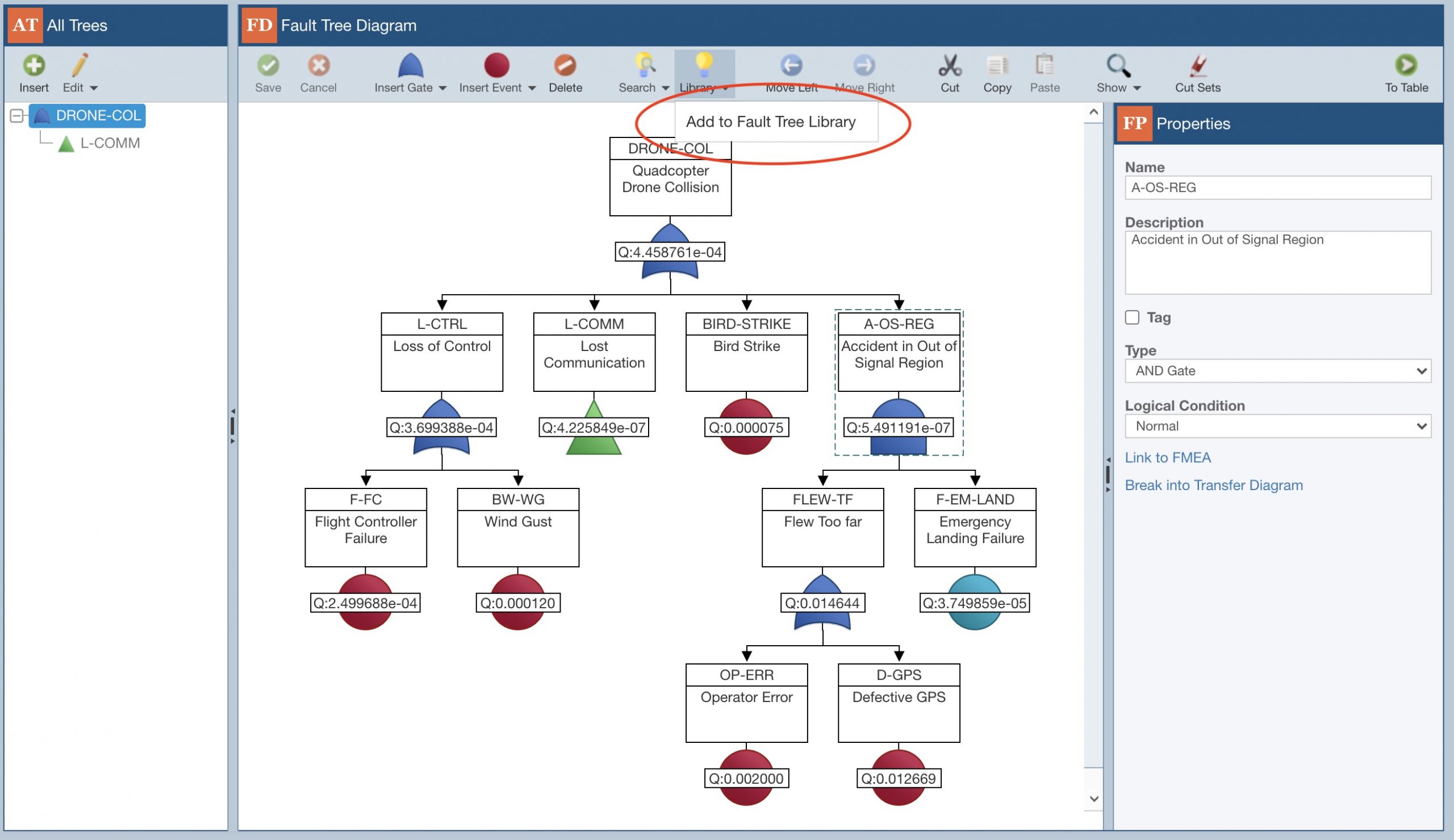
Also, you can selectively choose items from your Fault Tree Analysis to add to your Library. While working on your FTA, you can simply click the Add to Library option at any time to quickly and easily add an item to a Library.
Searching Fault Tree Libraries
The benefits of Fault Tree and Event Libraries become quickly apparent the first time you utilize the Library search and retrieve features.
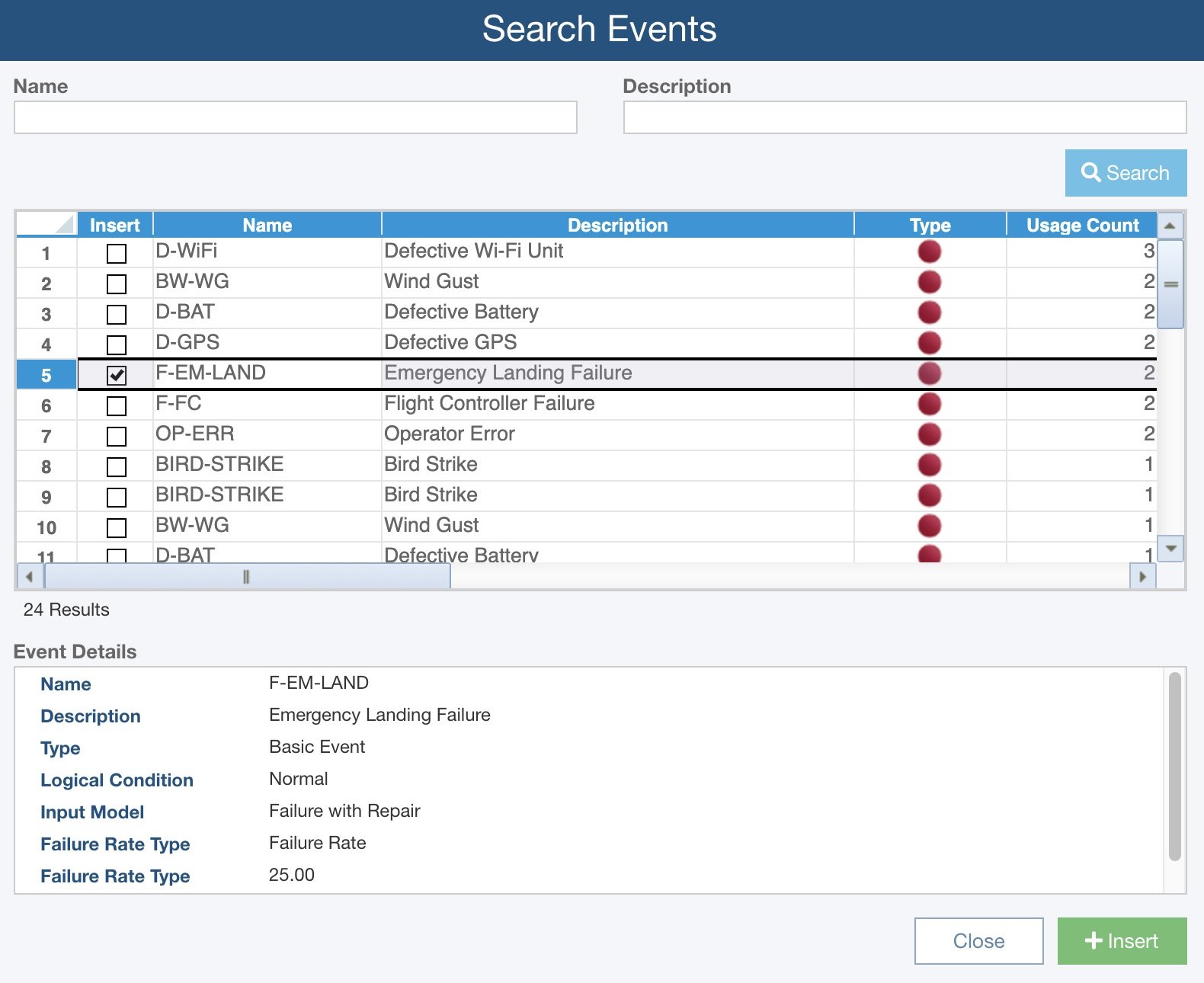
As you are constructing your fault tree, click the Search button in the Fault Tree toolbar to search either your Fault Tree Libraries or your Event Libraries. You then can filter your search based on a Name and/or Description. The matching items will appear and you can then select the item or items to insert in your fault tree.
This makes fault tree construction immeasurably more efficient, as well as more consistent.
Keeping Fault Tree Analyses in Sync with Library Data
Another significant advantage of Fault Tree and Event Libraries is the ability to keep all your fault tree data in sync.
For example, you may have an event in the Event Library that is used in multiple places in one fault tree or even in multiple fault trees. If any data associated with that event is updated, the change can be made directly to the Event in the Event Library and then pushed out to all FTAs using that Event.
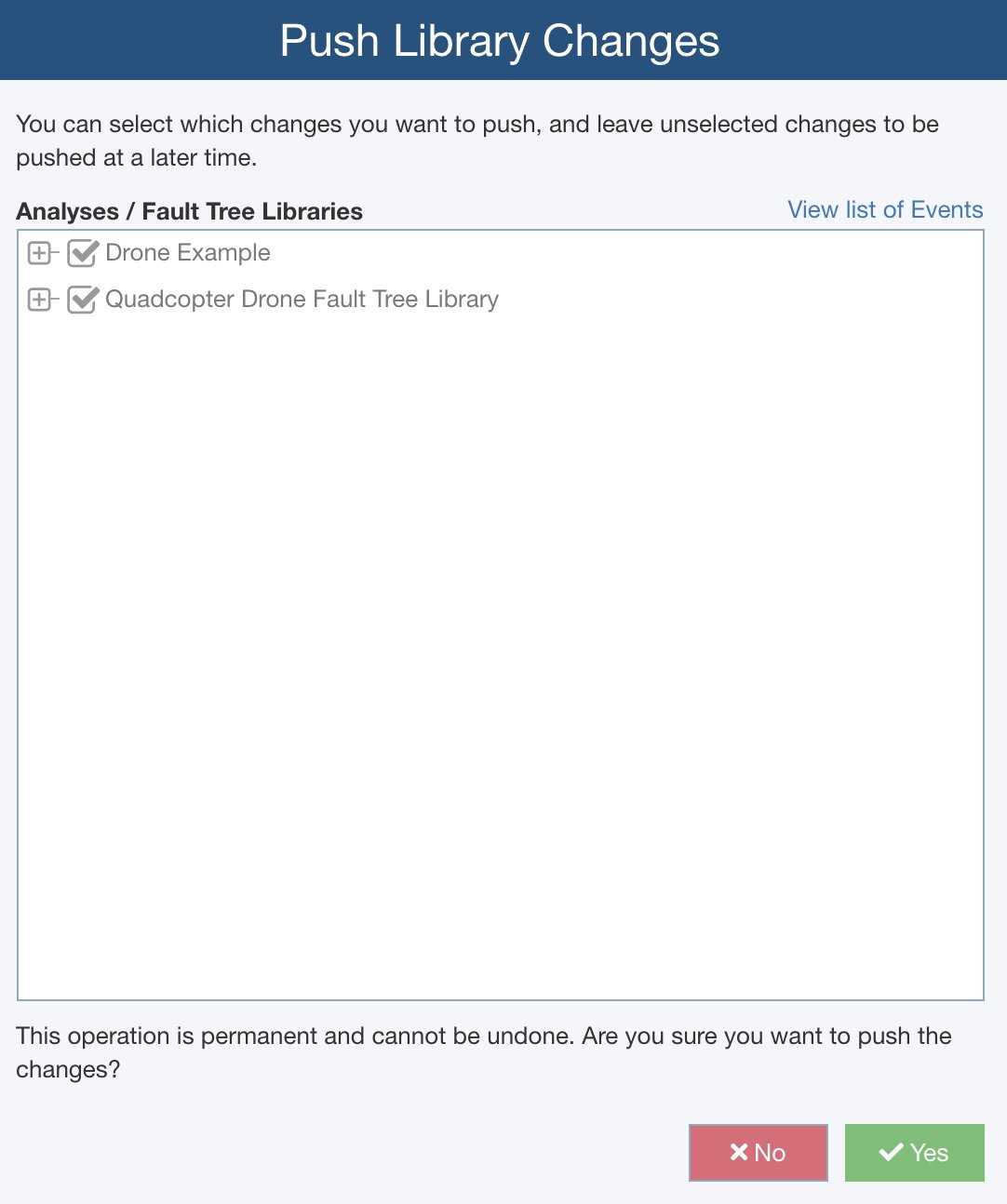
Additionally, the Push function allows you to select which pending changes are made. For example, perhaps a particular Fault Tree Analysis is pending review or under audit, and you do not want to make modifications until the review or audit is complete. In this case, you can hold off Push changes for that FTA to be done at a later time.
Viewing Fault Tree Library Links
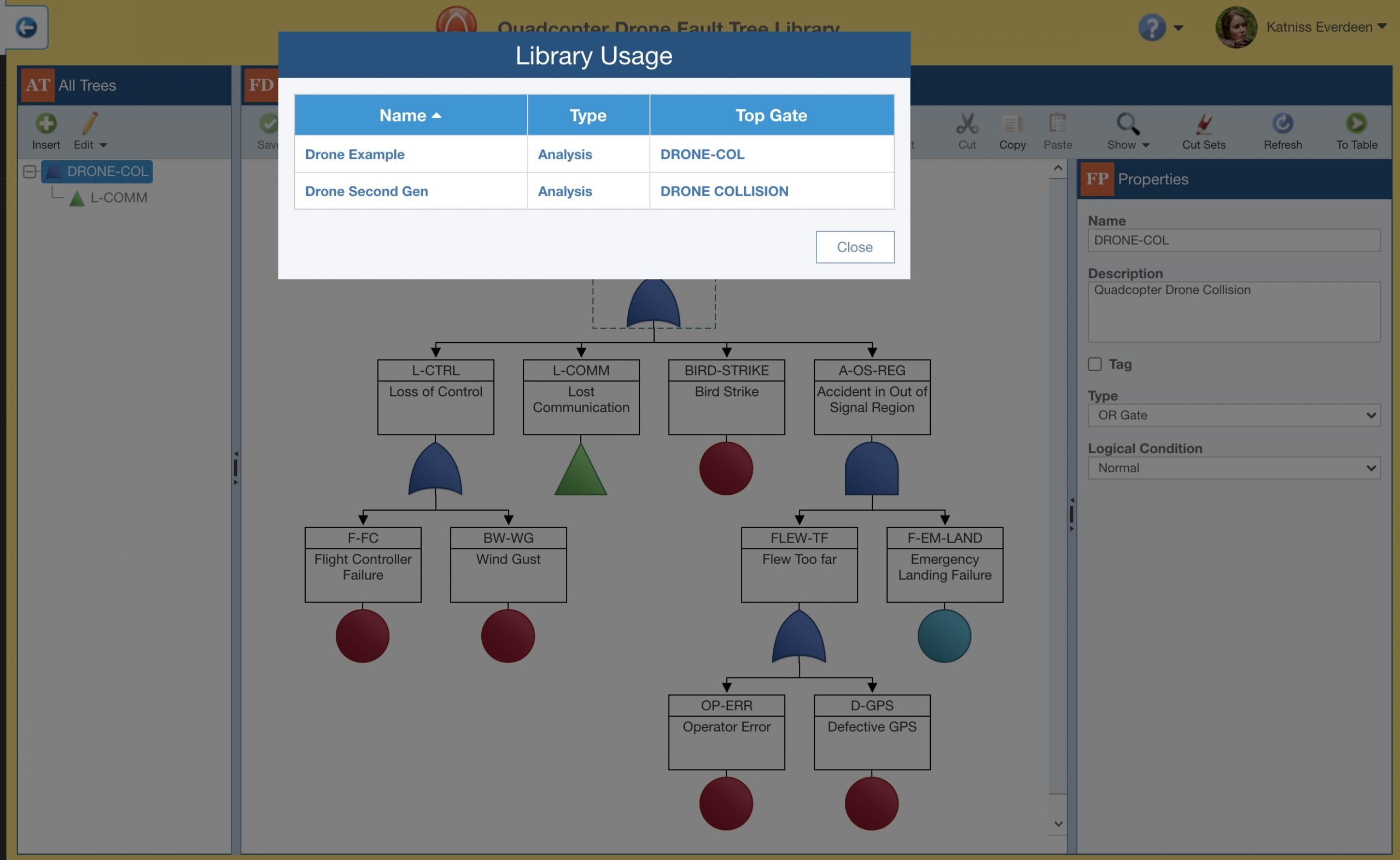
The Relyence Fault Tree Library View Usage capability enables you to view all the locations in your FTAs where Library data is referenced.
The View Usage function displays a list of all your Fault Tree Analyses and Top Gates that are linked to a particular item in your Library. This information is helpful to keep track how often your Library data is being used and what Analyses will be affected on a Push update.
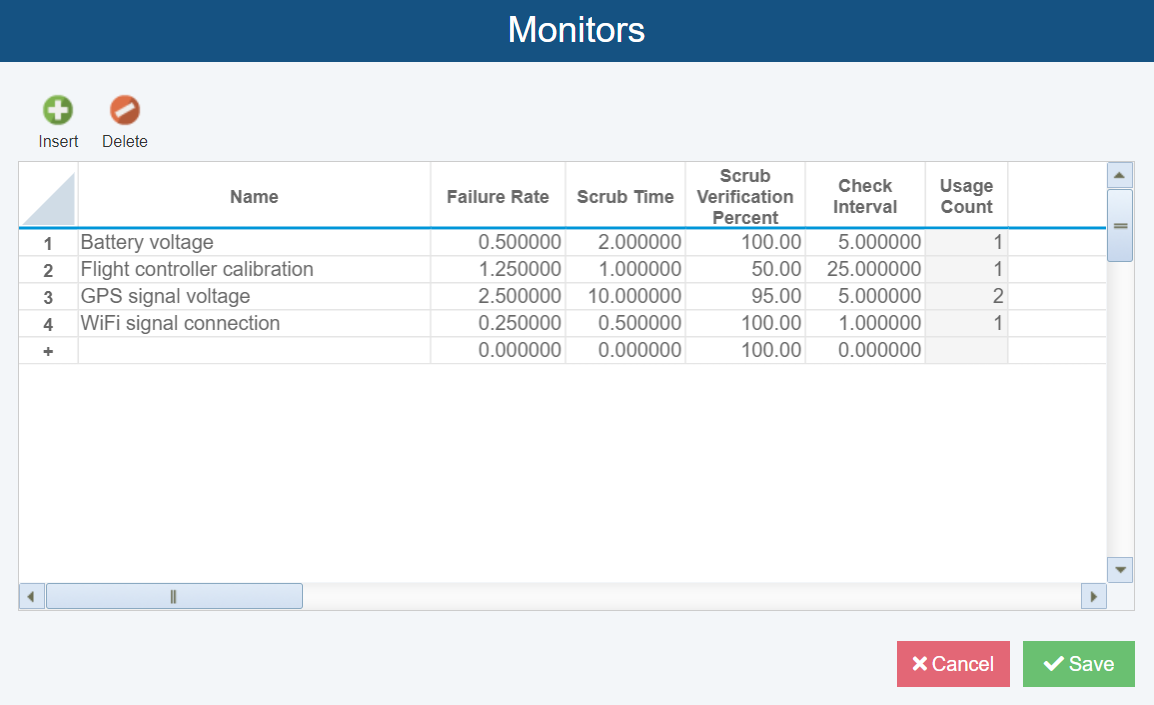
Monitor Libraries
When performing Fault Tree Analysis based on the guidelines provided in SAE ARP4754A / ARP4761, a latent failure is defined as a failure that is not detected upon its occurrence. They can often affect functions that are fail-safe or protective in nature and thereby, their occurrence increases the risk of a safety hazard.
To detect a latent failure, a monitor may be used. Monitors are methods to detect a latent failure, such as software, hardware, or other test methods. An example monitor would be performing a maintenance inspection to check a certain component’s condition.
The Relyence Monitor Library allows you to define and save a monitor with its associated parameters for later use. With the Monitor Library, you can easily share monitors between Events and can choose to treat each monitor as a Repeat or as its own unique copy in Fault Tree calculations.